Module 1,
Topic 1
In Progress
Physics
Linear kinematics
The analysis of linear motion without regard to its origin and effects is called linear kinematics.
Average speed
The average speed of an object is equal to the distance it covers in a certain time period divided by that amount of time.
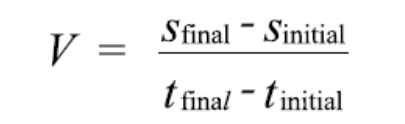
where:
V = average speed
s = distance
t = time
Constant acceleration
When acceleration is constant the equations relating distance and speed to time take the following forms:
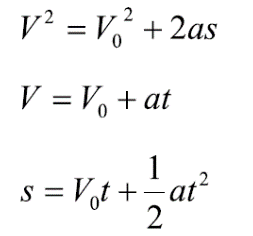
Where: V = speed V0 = initial speed t = time a = acceleration s = distance

